Last updated on February 5th, 2022 at 07:05 pm
Module 3 Ch 17/18 AC Generators.
[RICH_REVIEWS_SNIPPET category=”all”]
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/embed?listType=playlist&list=PLM1WlxRKWbFGjDK0Hac3O7XIYmZfuZ_qg[/embedyt]
Chapters
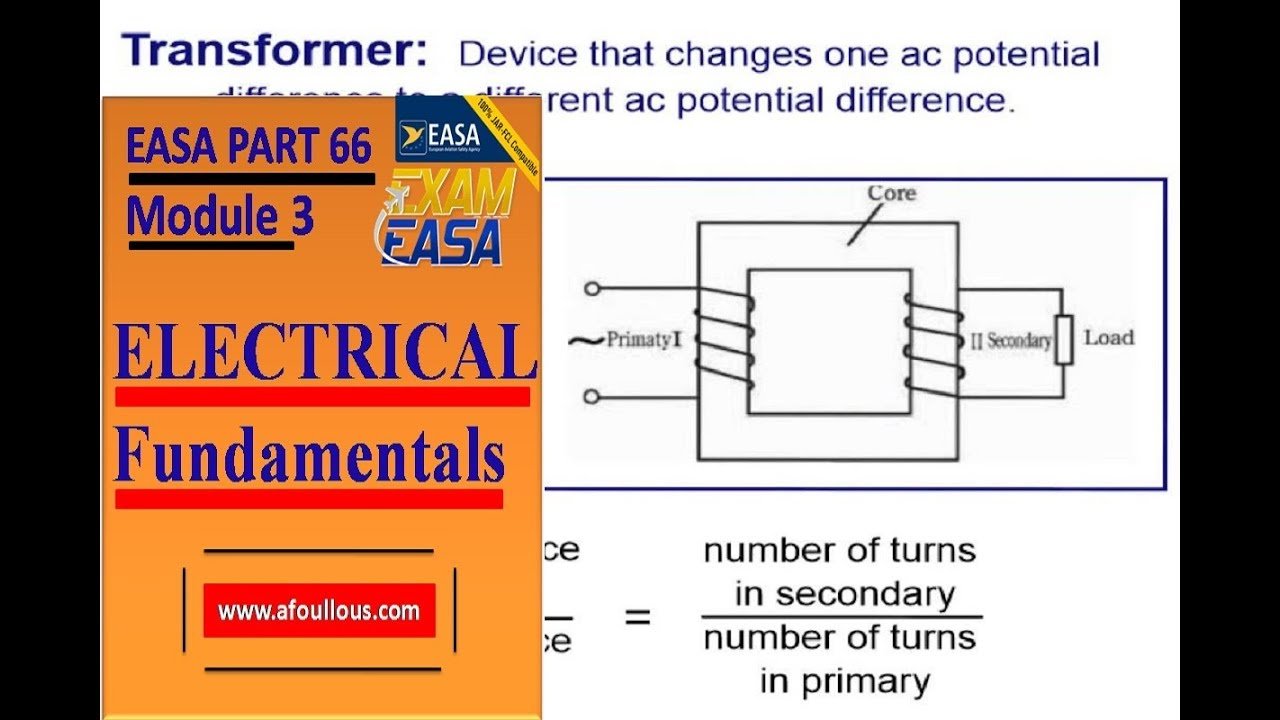
Chapter 15/18 : Transformers.
Chapter 16/18 : Filters.
Chapter 17/18 : AC Generators .
Chapter 18/18 : AC Motors .
Question and Training Exam
Sample – Electrical Exams ( 40 questions 30 min),
Category A – Electrical Exams ( 20 questions 25 min),
Category B1 – Electrical Exams ( 52 questions 65 min),
Category B2 – Electrical Exams ( 52 questions 65 min),
Category B3 – Electrical Exams ( 24 questions 30 min),
Book Store.
EASA Part 66 Module 3 Electrical Fundamentals Question Exam
Sample – Electrical Exams ( 40 questions 30 min),
Category A – Electrical Exams ( 20 questions 25 min),
Category B1 – Electrical Exams ( 52 questions 65 min),
Category B2 – Electrical Exams ( 52 questions 65 min),
Category B3 – Electrical Exams ( 24 questions 30 min),
Electricity Static Electricity and Conduction
First post and replies | Last post by Malika Benchikh, 7 years ago
EASA Module 3 Electricity:
ALTERNATORS
ALTERNATORS & CLASSIFICATIONS An electrical generator is a machine, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by electromagnetic induction. A generator which produces alternating current is referred to as an AC generator and, through combination of the words “alternating” and “generator,” the word “alternator” has come into widespread use easa module 3 electricity.In some areas, the word “alternator” is applied only to small AC generators. This text treats the two terms synonymously and uses the term “alternator” to distinguish between AC and DC generators. The major difference between an alternator and a DC generator is the method of connection to the external circuit; that is, the alternator is connected to the external circuit by slip rings, but the DC generator is connected by a commutator easa module 3 electricity.
METHOD OF EXCITATION One means of classification is by the type of excitation system used. In alternators used on aircraft, excitation can be affected by one of the following methods: 1. A direct connected, direct current generator. This system consists of a DC generator fixed on the easa module 3 electricity